Here we will learn about intersecting lines, including how to find the point of intersection of two straight lines and how to solve simultaneous equations graphically and algebraically.
There are also intersecting lines worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
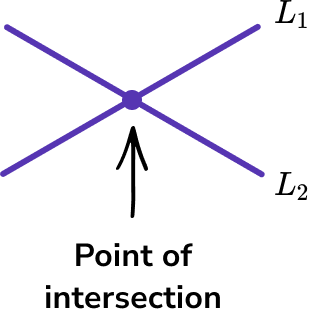
Intersecting lines are when two or more lines cross each other in a plane. There is one common point which lies on both lines which is called the point of intersection.
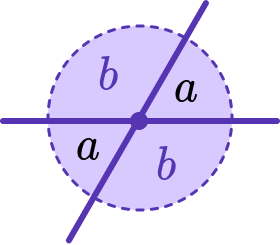
Two straight intersecting lines create pairs of vertically opposite angles (or vertical angles). One of the important properties of intersecting lines is that each pair of vertically opposite angles is equal.

In the Cartesian coordinate plane (using x and y, as we do at GCSE), two given lines l_ and l_ have either one intersection point, or no intersection points.
If a pair of lines do not intersect and have no common point, they are parallel.
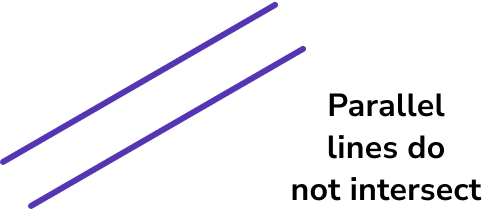
Remember that parallel lines have the same gradient.
Perpendicular lines intersect at right angles.
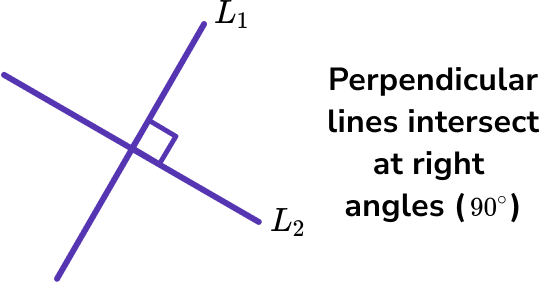
The product of perpendicular gradients is -1.
This idea links coordinate geometry to algebra work on simultaneous equations. If we are given the equations of two intersecting lines, or a graph of the two equations, the point of intersection of two lines is the solution to that pair of linear simultaneous equations.
In three dimensions, it is possible to have two lines which are not parallel but also not in the same plane – these are called skew lines, and will not intersect.